Troubleshooting and Bearing Damage Analysis
Because of widespread of bearing applications, it is extremely important to understand the mechanisms and root causes for their failures.
Importance of Rolling Bearing Damage Analysis
Rolling bearings are precision made and reliable engineering components that are produced in millions and used in almost every machine today. This is the reason for developing a particular branch of science that deals exclusively with rolling bearings technology. One benefit resulting form this branch of science is a possibility to calculate a life of a bearing with high accuracy. 90% of bearings should attain their design life. Therefore matching the life of a bearing with a life of a machine is possible. However it is not always the case. Because of the wide spread of bearing applications, it is extremely important to understand the mechanisms and root causes for their failures. A very clear benefit can be demonstrated as a consequence of better understanding bearing failures.
Some of these benefits do include:
1. A reduction in risk to personnel and equipment from a safety perspective.
2. The elimination and reduction of catastrophic machine failures
3. A reduction in maintenance cost by eliminating repairs.
4. A reduction in downtime by reducing the scope of repair.
5. An increase in production by scheduling repair at a time convenient to operations or when failure risk is at its lowest.
6. A reduction in downtime and costs by having advanced warning, which allows for thorough preparation and effective planning and scheduling of repairs.
7. A reduction in insurance cost.
8. The elimination of infective preventive maintenance as well as the increase between preventive maintenance occurrences.
Having all this in mind the International Organization of Standardization – ISO has recently (2004) published a international standard (ISO 15243) entitled “Rolling bearings – Damage and failures – Terms, characteristics and causes” in an attempt to standardize the nomenclature and to classify the failure modes occurring in rolling bearings.
The importance of the subject is such that there is a large number of articles and books written on it. However until recently (ISO 15243 in 2004) there was an array of different interpretations and nomenclatures for the same phenomena.
In the past 25 years I have been performing Damage Analysis for industrial clients. The majority of the failures are the result of a complex combination of factors such as design, manufacture, assembly processes, operation and maintenance, therefore experience is necessary to establish the root cause of the failure.
The process itself incorporates an exchange of information and material. The client provides the failed bearing (or part of) and a completed form MDM011 (available upon request from MDM Engineered soulutions).
We realize that to provide the most accurate damage analysis report, we must gather information about the bearing and assembly operating conditions as well as its maintenance history. As a result we require a completed MDM011 to secure that data.
Troubleshooting and Failure Analysis
MDM Engineered solutions provides independent and unbiased root cause failure analysis reports of bearings and power transmission components of all manufacturers.
We have an extensive library of bearing manufacturers publications as well as newest international standard (ISO 15243) edition of Rolling Bearing Damage and Failures.
When a bearing is damaged during operation the entire machine may seize or malfunction. Since bearings that fail prematurely cause trouble it is important to identify and predict failure beforehand so preventive action can be adopted and costly machine or system downtime avoided.
There are many possible reasons for bearing premature failure but the majority can be predicted and therefore prevented to occur.
Here are some examples of failed bearing components:
This inner ring on the right is of a spherical roller bearing. The bearing was under heavy axial load.
Spalling occurred on one raceway only.


The fretting corrosion on the outer diameter of a spherical roller on the left.
Developed as a result of micro movement between the bearing and the mating part (housing bore).
A typical occurrence on non rotating rings.
On the right is a inner ring of a bearing that exhibits heavy water damage. The etching is obvious and could be easily felt under the fingernail. It has developed in the contact areas between the rollers, grease and inner ring.


The inner ring on the left shows heavy plastic deformation as a consequence of inadequate lubrication.
On the right is a broken outer ring of a cylindrical roller bearing as a consequence of axial (thrust) force.

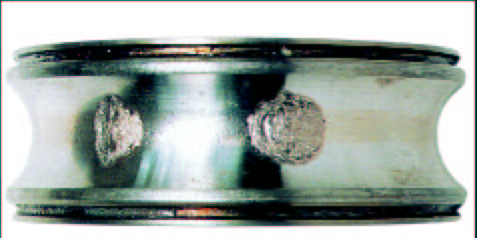
Inner ring of a single row ball bearing.
Localized flaking due to shock load during mounting.
On the right is a inner ring raceway of a spherical roller bearing. Circular shaped peeling pattern occurred as a result of marginal lubrication.
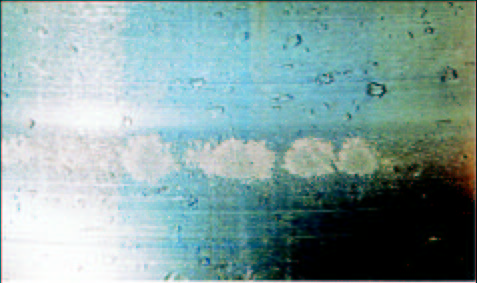

On the left is a cage of an angular contact bearing. Note the broken cage fingers as a result of misaligned bearing rings.
These balls are of a deep groove ball bearing. They are showing a dark colored electrical corrosion that is covering the entire surface of the ball.